It wasn’t that long ago when news outlets were abuzz with the idea that feminism was dead, a relic of the past.
Young women who had reaped the benefits of the Second Wave – access to postsecondary education, non-traditional jobs, boardrooms, and more flexible household arrangements – saw, it was said, no need to fight for more equality, more freedom. It was a “post-feminist” world. (I put that word in scare quotes because, as I explain below, “post-feminism” actually means something else among critically inclined feminists).
Of course, those commentators were dead wrong. But if they could keep their heads in the sand back then, they certainly can’t today.
Just 14 months ago Americans – well 26 percent of eligible American voters anyway – elected a man who has yet to meet a woman he hasn’t ogled, insulted, demeaned or groped.
Then, in 2017, high-profile, powerful men fell like dominos because the women they work with (and generally work in positions of relative power over) have been emboldened to tell their stories of sexual harassment and assault.
And although it gets far less press, it is also the case in 2017 – as it was in the 1980s when the “post-feminist” era was first proclaimed – that millions of women living in the wealthiest nations of the world face poverty, violence and/or discrimination in their everyday lives.
So, the post-feminist era was always a myth.
Even the pundits no longer talk much about “post-feminism.” They’ve actually found a new feminist – Justin Trudeau. And, more appropriately, Time magazine has just named the #MeToo movement its “person of the year.”
Of course, some of us have known all along that there is nothing outmoded about the need for a feminist analysis and politics. We’ve been working throughout the last few decades, advocating in various ways to improve women’s lives.
It is those “various ways” that I want to look at here. For however much one set of feminist politics tends to dominate the public discussion, there’s a rich and diverse tradition from which we can draw our ideas and thinking.
I’m going to comment briefly on three faces of feminist politics that have emerged over these years, which I’m calling:
- “Fearless girl” feminism
- Allyship feminism
- Anti-capitalist feminism from below
While there is plenty of overlap among these, we can trace their roots back to distinct theoretical and political premises – and in so doing, see how they support divergent notions of progress and freedom for women.
To signal where I’m going with this: while all three “faces” of feminism have generated substantive, material changes in women’s lives, it is the third approach – anti-capitalist feminism from below – that orients us to thinking about, how to develop a transformative politics that grapples most directly with the systemic nature of oppression.
“Fearless girl” feminism
The title here refers to the bronzed statue of a small girl facing off against “Charging Bull,” the Wall St. icon installed two years after the 1987 market crash. The “fearless girl” statue (created by artist Kristen Visbel) was erected by State Street Global Advisors just as International Women’s Day was rolling around this year. It symbolizes a feminism that promotes women’s “empowerment” through economic independence and labour market opportunities.

State Street Global Advisors is an investment firm which manages $2.5 trillion in assets. It unveiled the statue as the launch of a campaign to add more women to corporate boards of directors. (Apparently, surveys have found deep resistance to the idea that women should comprise even 50 percent of a board, with 53 percent of directors surveyed responding that women should comprise no more the 40 percent of board membership.)
Why would State Street Global Advisors care? Well, it turns out, gender diversity has been shown “to improve company performance and increase shareholder value.”
This is, of course, the dominant face of feminism today. It is what Justin Trudeau trumpets when he fills half of his cabinet seats with women (you’ll remember his flippant but hard-to-argue-with reasoning, “Because it’s 2015”). Or, when he sits down with Ivanka Trump for a roundtable on so-called women business leaders. Or, again, when he insists that any free trade deal with China requires both parties sign on to gender equity provisions.
And while many of us will roll our eyes at the superficiality of Trudeau’s feminism, few would argue, I suspect, that he shouldn’t take these positions.
In other words, it’s somewhat awkward, and complicated.
The so-called empowerment of women achieved by widening the corporate and political corridors to accommodate them is a result of decades of feminists trying to redress inequality through equal pay and pay equity legislation – legislation that has undoubtedly improved the lives of many, many women.
Yet, where has this gotten us? As the Trudeau/Trump collaboration attests, these feminist initiatives are easily coopted by a shallow exercise in corporate diversity management. And we see the broad societal impact of this uptake of “fearless girl” feminism in the widening gap between wealthy and average-income earning women.
Leslie McCall, a sociologist at Northwestern University, has tracked women’s wages in the US since the 1970s.
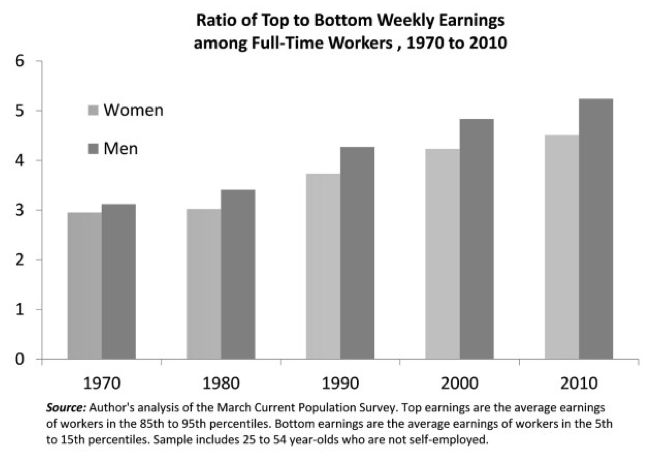
From: Leslie McCall, Men against Women: or the Top 20 percent against the Bottom 80, 7 June 2013, Council on Contemporary Families (https://contemporaryfamilies.org/top-20-percent-against-bottom-80/).
When she started, women with college degrees earned less than men straight out of high school. But then, the effects of equal pay legislation (introduced in 1963 in the US) started to kick in.
Today, women still haven’t seriously dented the ranks of the 1 percent. They are, however, much more often found among top salary earners. Women’s earnings in the top 85th to 95th percentile (yearly incomes of about $150,000) have grown faster than men’s earnings in that category in every decade since the 1970s. For example, they’ve seen a 14 percent growth in the first decade of this century, compared to an 8.3 percent growth for those making average wages.
According to McCall, there have been “strong absolute gains for women in this elite group.”
Meanwhile, median earnings of all full-time workers (men and women) didn’t change between 2001 and 2010. And the gap between high-earning women on the one hand, and middle- and low-earning women on the other, has been steadily growing.
So, while women who make about $150,000 a year are seeing their salaries continue to grow at robust rates, women (and men) who make about $37,000 or less a year have, for some time now, seen their incomes stall.
To be clear, then, we are talking about a very small proportion of women who have truly been “empowered” here:
- in 2013, according to a JPMorgan Chase researcher, only 3.25 percent of American women wage-earners took home more than $100,000 per year.
- That same year, according the US Social Security Administration, more than half of US wage-earners earned $30,000 or less. And you can bet that women, blacks, Latinos/Latinas, trans people, queers, and immigrants were over-represented in that group.
Yet, yet . . . I defend “fearless girl” feminism’s demand for pay equity and equal pay. One thing these figures don’t tell us – they can’t tell us in fact – is how much lower all women’s wages would have been had feminists not been fighting all along for economic parity and independence.
At the same time, it is awkward because while such policies have improved individual lives, they haven’t, and never could have, challenged the conditions which produce the tendency toward unequal pay in the first place – which is precisely why Justin Trudeau, Ivanna Trump, Hillary Clinton and Wall Street investment firms have no trouble with embracing and promoting them.
“Fearless girl” feminism is entirely consistent with the capitalist world order that Trudeau & Co. represent and defend. That is the same capitalist world order which can be pushed to accommodate some gender and racial equality, but cannot give up its life-blood: a vast and growing pool of low-waged, and no-waged, labour – and the racist, sexist and otherwise oppressive relations that ensure an ongoing supply of the same.
Allyship feminism
If we consider women’s experiences of violence and harassment over the same period that we looked at for changes in women’s wages (the 1970s to 2017), we find much less reliable statistical evidence. That’s because changes in women’s reporting levels fluctuate (recall how a couple high profile complaints at private sector companies led to the recent spike in reporting). It’s also because there have been shifts in how gendered violence is defined.
Still, we learn from a recent StatsCan report the following:
- Women’s reports to police of physical assault have fallen some, while reports of sexual assault are stable.
- The self-reported (on the General Social Survey) rate of violent victimization against women aged 15 years and over has remained relatively stable between 1999 and 2009.
Most significantly, we know that gendered violence and harassment continues at unacceptable levels today. A report by the Canadian Women’s Foundation tells us that:
- Half of all women in Canada have experienced at least one incident of physical or sexual violence since the age of 16.
- Approximately every six days, a woman in Canada is killed by her intimate partner.
- There are upwards of 4,000 murdered and missing Indigenous women in Canada.
- Young women (aged 18 to 24) are most likely to experience online harassment in its most severe forms, including stalking, sexual harassment and physical threats.
While there have certainly been missteps, and there is still much more that needs to be done, feminists have demanded and won resources for those vulnerable to gendered violence. They have also developed policies and practices that make meaningful differences in the lives of women, trans people and queers, allowing many to leave risky, abusive situations, to better negotiate legal systems, and to feel more secure at school, on the streets, and at work.
In recent years, much of that work has been informed by what I’m calling allyship feminism (though other forms of feminism certainly deserve credit too for progress on these fronts). By allyship feminism I mean to identify a politics that is grounded in a critique of intersecting systems of oppression. Similar to anti-capitalist feminism from below, this feminist perspective sees the powerful institutions and practices in our society – schools, courts, law, corporations, healthcare – as implicated in upholding racism, sexism and heterosexism, trans and queer phobia, ableism, settler colonialism, economic exploitation, and so on. [1]
However, even though many feminist allies hold this radical, often even anti-capitalist, understanding of society, their political work usually stops short of challenging the systemic powers they critique.
The reason for this arguably has much to do with their commitment to the principle of allyship, and the ethos of “privilege” that informs it.
Allyship feminism begins with listening to those who are directly disempowered in this multiple and complex matrix of “interlocking” oppressions (to use Patricia Hill Collins’ term). Listening is integral to a process of building relationships of trust and accountability with those feminists seek to be in allyship with. Once that relationship is on solid ground, then feminist allies engage their financial, organizational or other forms of resources to help strategize ways and means to support and protect the disempowered.
This approach is counter-posed to mainstream feminism, which tends to treat the marginalized as victims or clients, who can be helped by integrating them into existing institutions and systems. By contrast, the goal of allyship feminism is not to “save” or “integrate” people, but to work with them, on terms defined by the marginalized, to “challenge larger oppressive power structures.”
It is also counter-posed to the (presumed masculinist) socialist left. Rather than “impose” their systemic critique on the oppressed, and prioritize political confrontation and social change over meeting the self-defined needs of marginalized communities (as certain – though, significantly, not all – left traditions can be rightly singled out for doing), allyship feminists stress that their own political goals are secondary to those they seek to be allies with.
Alongside offering resources, feminist allies actively work to recalibrate interpersonal relationships between themselves and marginalized people. This means, in the first instance, identifying and taking responsibility for one’s complicity in the wider social dynamics of oppression – for one’s “privilege,” say, as a white, able-bodied, cis-gendered student who is working with Indigenous women living in poverty.
“Checking one’s privilege” is not an optional or one-time feature of allyship feminism. According to the Anti-Oppression Network, allyship is “an active, consistent, and arduous practice of unlearning and re-evaluating, in which a person in a position of privilege and power seeks to operate in solidarity with a marginalized group.”
Self-consciousness, care and respect when working with vulnerable people is incredibly important. What’s more, there is no doubt that the work of feminist allies has made university campuses, workplaces, homes and streets safer for many women, queers, and trans people vulnerable to sexual assault and harassment. It has contributed to establishing and improving funding for community centres, safe spaces and educational materials about gendered violence. It has led to improved policies and procedures for those reporting sexual assault, and contributed a compelling defense of nongendered language to an often toxic public debate.
But, again, I find assessing allyship feminism to be a bit awkward and complicated. As with struggles for pay equity and equal pay legislation, this approach hasn’t been – and can’t ever be – enough. Allyship feminism comes up against the limits of its own premises.
First, the focus on using resources to support the goals of more marginalized people is laudable of course. But it can – and often does – work to bind feminist allies to the very power structures that perpetuate the inequality of resources that have made them “allies” and not members of the “more marginalized” communities in the first place.
Instead of confronting power, feminist allies tend to define their political work in terms of getting those in positions of authority onside with their agenda. They risk cultivating, that is, either a naïve trust in their bosses or political elites (who they believe they can influence), or a fear of alienating the support of their higher-ups by pushing for more radical demands.
Second, the politics of individual privilege risks diverting attention away from the broader forces sustaining the conditions of inequality and oppression. Feminist allies insist that “checking one’s privilege” is about taking responsibility for one’s own consciousness and behaviour, and not about confessing guilt for occupying a relatively advantageous social position.
But, as critics of this approach point out, the focus here is nonetheless on the individual. And not just any individual. Because it is their “self-changing” which becomes the centre of political work, say the critics, feminists from the dominant (usually white, academic) culture have (once again) made themselves the centre of anti-oppression politics – albeit not intentionally, nor in the same way as “second-wave” feminists did. Still, the irony is hard to miss.
In some ways, privilege politics grows out of another second wave feminist idea, the idea that the personal is political. Understood as a claim that our most intimate relations are conditioned by wider power dynamics, that maxim is, I believe, indisputable. But insofar as allyship feminism focuses on personal privilege as a site of political activism, it suggests something else. It suggests that power is everywhere – an idea most associated with the French political philosopher Michel Foucault (1926 – 1984).
According to this perspective, there is no essential difference between the “power” wielded by individuals caught up in systems of oppression on the one hand, and the power generated and/or sustained by broader political and economic dynamics on the other. Or, if feminist allies do consider these types of power as distinct in some ways, privilege politics tends to obscure the relationship between them. As a result, key questions about systemic change tend to go unanswered: does, for example, challenging individual interpersonal practices and language lead to wider, more systemic, change? If so, exactly how?
The limits of allyship feminism are thus considerable. Yet, it is hardly surprising that many of the most critically minded feminists are drawn to this set of politics today. For those limits reflect the general weakness of the wider left. They reflect a left that has largely lost the capacity to pose an alternative to the broader structures of power that allyship feminism critiques.
My point is not that we need to, or should, abandon the type of work so many feminists with a radical critique of society do. While we should challenge some of their strategies, I think they advance important lessons for the wider left about working for social change within institutions, and about building relationships with disempowered communities.
The key task is to figure out how such work can be part of a broader challenge to the systemic reproduction of multiple oppressions. How can this work help build the societal capacity, confidence and solidarity required to move beyond where we find ourselves today?
Anti-capitalist feminism from below
Of the three faces of feminism, this is certainly the least familiar. That’s in part because, for the last 50 years, socialist feminists have gone from being a coherent presence on the left to working within organizations dominated by other sorts of politics. Unions and labour councils have absorbed many, but so have some activist groups mobilizing around healthcare, education, and poverty. And you’ll still find socialist feminists, like myself, lingering in small left groups like the New Socialists and, of course, in the academy.
By “coherent presence” I mean that anti-capitalist, from-below, principles contributed to and sometimes guided feminist political action in the 1970s and 1980s. Certainly, in Toronto, the struggles to establish childcare centres at the University of Toronto, to get maternity leave provisions in contract negotiations, to demand access to abortion, and to oppose police raids on bath houses are great examples of that.
In all cases, socialist feminists argued for and won arguments about the need to call out and confront those in power through large mobilizations. The idea was not to ask for spaces and services so much as it was to collectively claim them.
I don’t mean to romanticize this. To begin, these gains, like those of all feminisms, are fragile. As well, there were lots of unresolved issues, including a marked inability (and less commonly, a refusal) to seriously deal with the multiple and sometimes contradictory forms of oppression. That failing contributed to the dismantling of socialist feminist organizations and the faltering confidence that a broader vision of freedom from oppression was even possible.
In the last five years or so, though, we’ve seen a smouldering interest in the ideas of a renewed socialist feminism. By renewed, I mean a socialist feminism that doesn’t simply repeat the insights of an earlier era, but learns from its shortcomings, and attempts to move beyond these – namely, to deal seriously with the complexity of oppression.
This renewal, however, has had only a limited political expression. Many anti-capitalist feminists from below working in community and labour organizations today have renewed this face of feminism in practice, by building solidarity among feminists, anti-racists, queers, trans people and others. But they have not often articulated the principles guiding their work in any sort of coherent set of socialist feminist politics.
That task has been taken up largely by those of us in the academy and parts of the organized left. We are now debating and discussing the version of social reproduction feminism that was initially framed by Lise Vogel, in her book Marxism and the Oppression of Women. More on that in a second.
While one might argue that the numbers of US women who rejected Hillary Clinton and her fearless girl feminism, and flocked instead to the Bernie Sanders campaign are a sign that times are ripe for such a feminism, to date, in North America, the most significant political expression of anti-capitalist from below feminist politics came with the March 8, 2017, call for an International Women’s Strike.
The North American organizers of that strike took their inspiration from three mass mobilizations in 2016: the Polish women’s strike, which stopped legislation to ban abortions in that country; the Black Wednesday strike called by the #NiUnoMenos, (Not One Less) movement in Argentina to protest male violence; and the 300,000 Italian women and supporters who mobilized on the International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women.
The organizers also understood that the sea of people donning pussy hats in the Women’s March this past January were not just upset that Trump was in the White House instead of Hillary Clinton. Their chants and placards drew attention to the devastation neoliberalism has wrought on the lives of women, trans people, Indigenous peoples, blacks, queers, immigrants and migrants.
Building upon all this, a group of US-based socialist feminists took up the call (issued first by the organizers of the Polish strike) for an International Women’s Strike. The call for a “strike” was deliberate. It was intended, according to one of its organizers, Cinzia Arruza, “to emphasize the work that women perform not only in the workplace but outside it, in the sphere of social reproduction”. That is, it highlighted the unpaid and/or low-waged work of cleaning, cooking and childminding (among other things) that produces the key thing capitalism needs in order to realize a profit, the worker.
Anti-capitalist feminism from below takes that insight as its starting point – an insight of social reproduction feminism that is articulated particularly well by Lise Vogel. Briefly, Vogel argues that capitalism absolutely requires workers, but bosses do not directly control their production (that is, the daily and generational renewal of labour power). That renewal is organized in patriarchal, heterosexist and racialized ways primarily in households, but also in hospitals and schools, for example, and through migration regimes.
Moreover, the relentless drive to exert a downward pressure on wages (and also on taxes) means that although capitalism needs workers, it also cannot help but undermine the capacity of those workers to reproduce themselves. And it is this unresolvable contradiction between the production of value and the production of life that haunts capitalism, making oppression a systemic feature of its very existence.
The 2017 International Women’s Strike – in recognition of the centrality of women’s work to capitalism – called on women to withdraw their labour not just from the workforce but from sites of unpaid social reproduction too. And women around the world responded. Activists in fifty countries participated.
While mostly symbolic as one-day protests tend to be, the strike as a strategy drives home the point that feminism can have an insurgent face that calls out the systemic nature of oppression.
And if we agree that it is capitalism that limits the possibility of meeting the very real survival needs of people, that puts profits before need not just in the workplace but in our communities and homes, then confronting that system also requires confronting the racism, sexism and all oppressions that work in concert with capitalism and against life.
This means working for greater economic equality between men and women, and to provide safe spaces and adequate resources for marginalized people. But we need to organize the demands for these things in ways that also build peoples’ capacities to draw attention to the ways in which oppression is embedded in the capitalist mandate to put profit over the meeting of human need.
And the only way we will ever be able to challenge that is by drawing more and more people into struggle – building the confidence and capacity of everyone with a stake in a more just society – to claim back not only our workplaces, but also our communities (our hospitals, schools, streets and households).
This doesn’t mean imposing ideas on marginalized groups. It does mean discussing and debating the nature of social power with them – and then strategizing to find ways to build the collective confidence to claim back the economic, political and cultural resources needed to produce a better world.
To my mind, this is the key distinction between working in solidarity with groups and seeking out allyship with them. Building solidarity certainly involves listening and respecting the self-determination of distinct groups. But it also involves moving beyond offering support and help, to articulating shared goals and strategies based on the knowledge that (i) all our lives are organized in and through a broader set of distinct, but nonetheless unified power relations; and (ii) that the capitalist system organizing those relations denies us collective control over the resources required to socially reproduce ourselves and our worlds in a way that meets our (material, cultural, spiritual, physical – in short, human) needs.
Solidarity, then, means standing with those who are willing to disrupt the usual flow of power from top to bottom. Black Lives Matter, Idle No More, the Quebec Student Strike – these are all examples of recent efforts to reclaim social reproductive space and resources (our communities and schools) through movement building.
We can improve lives through influencing those in positions of authority to grant certain things – better services and education, higher wages and benefits. And we should continue to do that. But if we don’t link those struggles with others that also challenge more directly those who hold power over us, the patterns of inequality and oppression that keep far too many women, blacks, migrants, Indigenous and disabled people disempowered, and living in poverty and fear for the last fifty years, will still be evident over the next fifty.
In the era of Trump and Weinstein, we need the face of feminism to be insurgent and transformative.
[1] The feminist “post-feminism” that I referred to earlier (not to be confused with the media popularization of that term) takes its lead from intersectionality theory. Feminism is considered outmoded not because it is no longer needed or relevant, but because it is too narrow. That is, the implied privileging of gender relations is too narrow to adequately address the multiple, complex interaction of oppressions that more accurately describes people’s experiences.
Sue Ferguson is a member of the Toronto New Socialists, and writes on social reproduction feminism.
This article is based on a talk given on Dec. 8, 2017, sponsored by the Ottawa New Socialists and University of Ottawa PIRG.
Photo: mronline.org


